Hi Everyone,
With a slight delay but we’ve got it 😄
Last week, I attended the Summer School on Illicit Trade organized by the University of Groningen and The Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime (GI-TOC).
I honestly thought I signed up for a regular course, I had no idea how selective or global it was! Participants from every continent, full engagement, and a packed agenda. Fun fact: the last edition was held in Warsaw 😄
I also didn’t expect to find myself learning OPSEC & PESEC at NATO HQ shortly after mentioning NATO in a previous newsletter 😄
We had sessions with United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), OSINT & AI workshops, and presentations from Dr. Tim Wittig (RUSI) & Dr. Francesco Giumelli (RUG) - organisers and Bernie Kaussler, ING’s Intelligence and Investigative Division (Congo case), Basel Institute on Governance (capabilities of i2 Analyst’s Notebook), and Schiphol Airport (wildlife smuggling monitoring).
We visited European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF) as well. For me, it was fascinating to hear how they deal with counterfeiting cases. I’ve previously worked more from the practical side: OSINT, reaching out to potential scam sellers, ordering samples, conducting due diligence, and testing bulk purchases.
The program focused on four major areas:
drug trafficking (cocaine, synthetic opioids, captagon), arms trafficking & dual-use goods, wildlife crime, and human trafficking.
My final research report and 60s elevator pitch focused on illicit arms trafficking in Kosovo - a backdoor into Europe that is also used for drug trafficking.
This was the 8th edition of the program.
On top of that, last week Frontstory and Vsquare published an investigation we had been working on for nearly a year. It’s honestly one of the most difficult stories I’ve ever worked on → details below.
Cybersecurity News
McHire exposed: McDonald's job platform McHire leaked data from over 64M applicants due to default credentials (
123456) and an API flaw. Find out more.Update v18 of MITRE ATT&CK (Oct 2025) brings a major shift in how detection models are structured. Modern detection isn’t about single-line rules anymore. They're introducing a scalable, structured approach with modular STIX objects and versionable detection strategy blueprints.
Find out more.
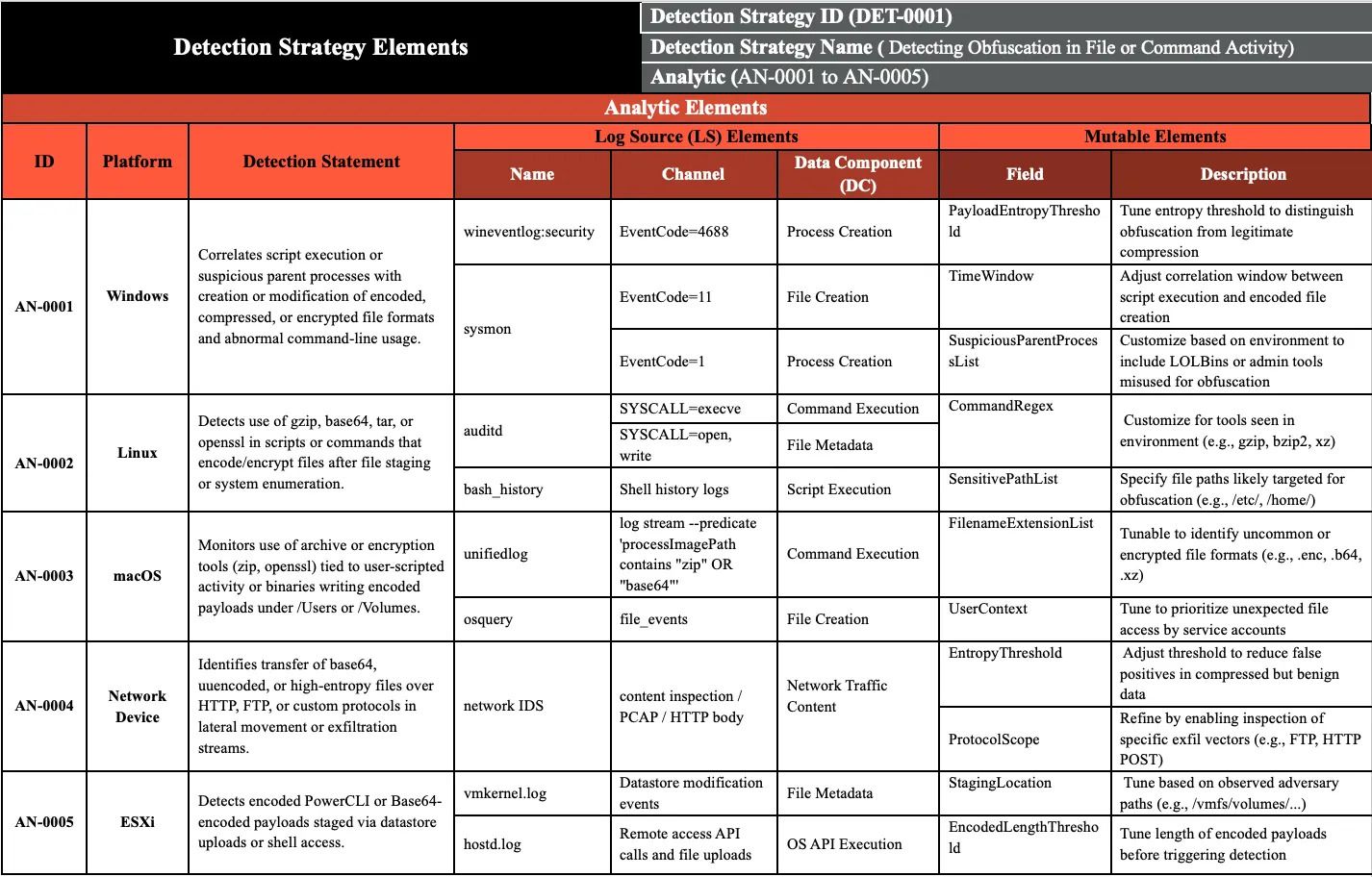
Table 7: T1027 Obfuscated Files or Information Example
Vulnerabilities & Exploits & Hacks
Sudo flaws fixed: Two local privilege escalation bugs (CVE-2025-32462 & CVE-2025-32463) patched in Sudo. Find out more.
Fake VS Code extension: A spoofed "Solidity Language" extension for Cursor AI stole $500K in crypto using PureLogs malware. Find out more.
Threat Hunting & Malware
SEO poisoning campaign: 8,500+ websites compromised in a widespread SEO poisoning campaign to distribute malware via search engines. Find out more.
Acquisition & Funding
Grammarly x Superhuman: Grammarly is acquiring email startup Superhuman to build an AI-powered productivity suite that goes beyond grammar checking. Find out more.
LevelBlue acquires Trustwave: On July 2, 2025, LevelBlue, a global AI-driven managed security leader, agreed to buy Trustwave from MC2 Security Fund, becoming the largest pure-play managed security services provider. Read more.
📰 Reports
AIVD Annual Report. 2024: The Dutch intelligence service (AIVD) has published its 2024 annual activity report. Read the report.
Czech BIS Report 2024: The Czech Security Information Service (BIS) has released its annual report detailing intelligence priorities and activities for 2024. Read the report.
Espionage & Counterintelligence
Russian espionage in Sweden: New reports from FRANCE24 highlight alleged Russian espionage activities involving a church near Stockholm’s airport. Find out more.
Poland launches first SIGINT ship: Poland has launched its first signals intelligence (SIGINT) vessel, one of two built in Gdańsk by Swedish defense firm Saab. Find out more.
Russia and the Taliban: In April, Moscow removed the Taliban from its list of terrorist organizations. By July 2024, President Putin called the group “allies in the fight against terrorism.” Find out more.
US Secret Service and crypto crime: The U.S. Secret Service has quietly emerged as a major force in combating digital financial crime, becoming a leading “crypto cop” amid rising fraud. Find out more.
DroneShield expands in Sydney: Australian counter-drone technology company DroneShield is investing $13 million in a new Sydney manufacturing facility to meet growing demand for its defense solutions. Find out more.
SOCMINT
Russia’s new social app “Max” launched
Russia quietly introduced “Max,” a domestic alternative to Western social media platforms. Details on its features and user adoption are still limited. More info“Tea” app monetizes dating safety: The dating safety app Tea started as a Facebook group and now generates over $200,000 in monthly revenue with 1 million users. It enables women to anonymously search men's names, verify identities, and purchase background checks. Features include reverse image lookup, criminal history reports, and sex offender registry scans. Female verification is required to access the service.
Age verification
Australia tests search age checks: Australia is quietly rolling out mandatory age verification for search engines like Google.
Reddit verifies UK users' age: Reddit now requires UK users to prove they’re 18+ to access mature content under new safety laws.
EU pilots age-check app: Five EU countries will test a unified age verification system to better protect children online.
OSINT
Doxing - a form of information warfare? Where does OSINT end and doxing begin?
The line isn’t about tools - it’s about intent and consequences.
OSINT (gathering public data) turns into Doxing when it deliberately puts others at risk (e.g. by exposing personal information such as home address, phone number, or family details with the intent to harass, intimidate, or endanger the person).
Our story is the result of a months-long investigation by FRONTSTORY.PL, Vsquare, and the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism, supported by the European Media & Information Fund (EMIF).
As part of the ANTI-DOX project, we studied how Russian actors collect data, spread it, and use psychological targeting online.
For me, this was the most challenging investigation I’ve worked on. I could sense the data was connected but it took time to understand how. The hardest part was interpreting the evidence and communicating it clearly to the team, knowing the threat was real and ongoing.
A breakthrough came through our collaboration with DomainTools. Thanks to joint analysis, we linked one of the doxing sites to an individual: Oleg Makarov a discovery that pushed the investigation forward. Here’s our the technical writeup
🔍 My pivoting process – tracing Oleg Makarov step by step:
After WHOIS was deprecated (Jan 2025), we used RDAP and Domaintools to look into domain history for
wartears[.]organdforeigncombatants[.]ru- which collect and publish names, addresses, and photos of both Ukrainian soldiers and foreign volunteers often labeling them “Nazis” or “mercenaries”.One phone number in the domain record led to a Telegram account with “co-founder of Project1 & Vatfor” in the bio.
That same user had posted in 2020 on a Telegram group for Project1, sharing instructions on how to build a site using Wikimedia backend — the same method used for
foreigncombatants[.]ru.An email address connected Oleg to Vatfor, and open sources confirmed he was listed as a co-founder.
Searching further, I found a Russian data leak from this year discussed in local forums - users were complaining about how easy it was to access personal info.
Through a Russian pastebin, I found a matching data set: full name, address, DOB, company name, and number.
DOB couldn't be verified via cross-sources, but other Vatfor co-founders had matching birth years (±1 year).
The company’s listed number pointed to a specific Russian data center. I then found archived mailing lists showing admins discussing infrastructure including our target’s full name.
Finally, a reverse image search linked to Oleg’s 2015 blog and public Instagram, where he discussed working on these kinds of administrator netowrk projects.
In this case, the POI (point of interest) provided most of the data himself. I used that to my advantage, applying google dorking (mainly via yandex and bing, which yielded better results than google), as well as tools like osint industries and pimeyes.
The final graph:
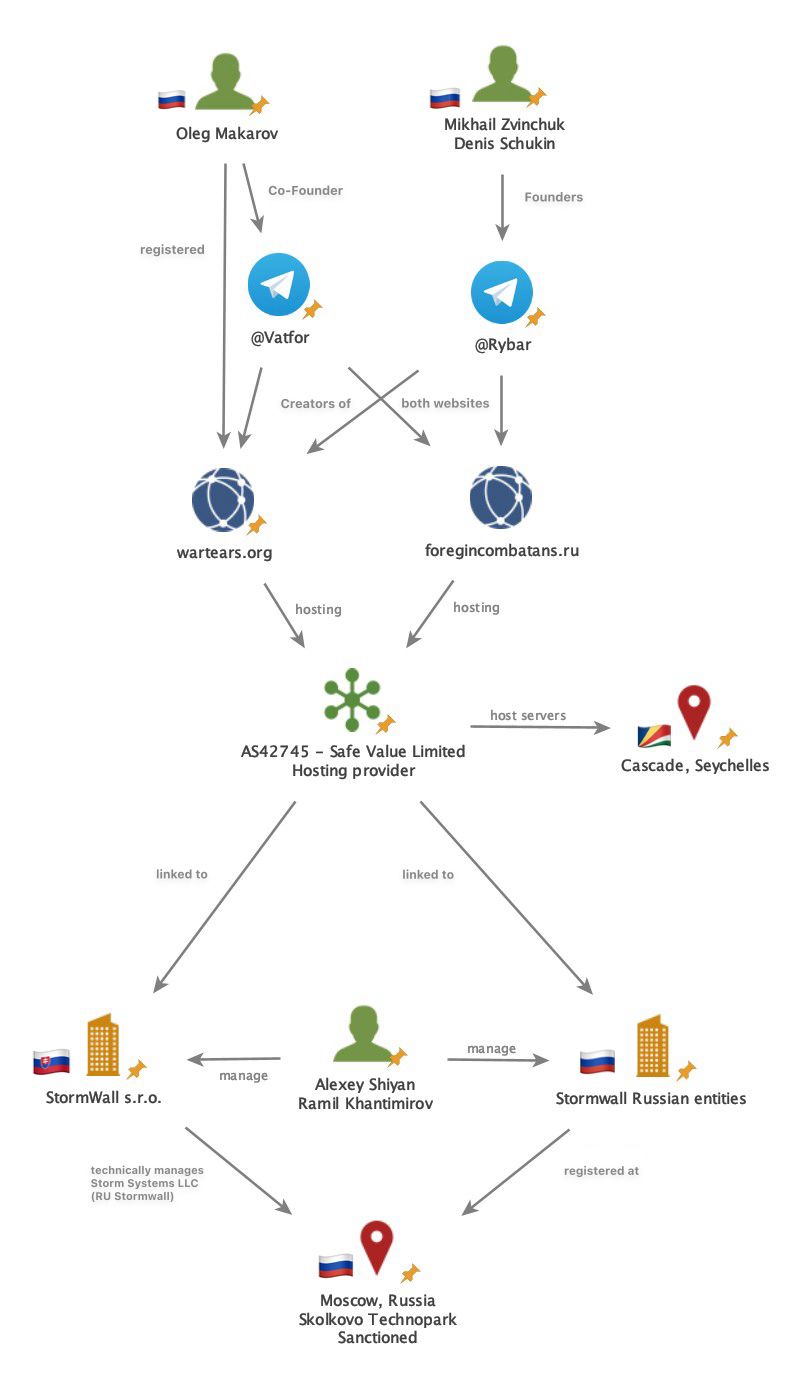
We are creating a follow-up article focused solely on Stormwall. We'll dive deeper into its connections and investigate which other domains and platforms it may be tied to.
Google Updates
Google explores Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Google is developing privacy-preserving authentication using ZKPs to enhance secure data validation.
Google ends fact-check snippets: The company has removed fact-checking snippets from search results, raising concerns over misinformation.
Google tightens HTTPS certificate rules: New enforcement measures will require stricter web certificate compliance to improve browsing security.
Darknet
Darknet Kingpin used ID cards sourced from Darkweb for Drugs Trade: A kingpin involved in the Ketamelon drug trade was found using ID cards obtained from the dark web to facilitate illegal activities.
Dark Web Retaliation: AntiDark targeted by 'United States of Dread'
AntiDark, a community known for exposing cybercriminals on the dark web, had its site defaced by a group linked to Dread - a major dark web forum often described as the “Reddit of cybercrime.” Calling themselves the United States of Dread, the attackers claim they unmasked three AntiDark administrators in response to doxxing of dark web users.
Upcoming CyberSec / OSINT Events
Free
Doxing as a new tool in Russian Influence Operations
Experts will explore how doxing is used in modern Russian influence campaigns. July 16, 11:00–12:00 CET, Webinar Info - It will be recorded.
Teaching OSINT Summit – OSINT Foundation
Leidos Global Headquarters, Reston, Virigina ; Restricted to U.S. Citizens Only.August 6th from 9am to 4pm More Info.
EU CyberNet Club #44: OSINT – Free Webinar by EU CyberNet
A session focused on OSINT techniques and best practices across EU contexts. 7 August 2025 14:30 (CEST) Webinar Info.
Paid
UK OSINT Community: War, AI & Dirty Money – In-Person Meetup
Panel discussions on conflict, artificial intelligence, and financial crime investigations. July 24, 17:30–00:00 BST, London Register here.BruCON Security Conference – 2-Day In-Person Event in Belgium
International conference on cybersecurity, hacking, and incident response.
Sept 25–26, Event Info.
🙃Bonus
Bellingcat is launching new challenges in July

